El Hallux Valgus, comunmente conocido como juanete, es una prominencia (un bulto) que aparece en la parte interna del pie, just before the first toe (big toe). This bump is due to a more complex deformity called hallux valgus, which consists of an outward deviation of the first toe, caused by an inward deviation of the first metatarsal.
What causes it
Footwear: Pointed-toe shoes with high heels are one of the important factors in the appearance of bunion symptoms, but they are not the only cause of their appearance.
It is a problem that is due to many factors, which include: heredity, sex, foot shape (Egyptian foot and flat foot), strength or weakness of the ligaments and tendons (ligament laxity), alterations towards the back of the foot and ankle such as instability of the metatarsal bone joint, among others.
It's very important to be aware of the most important fact: regardless of the cause, people with bunions DO NOT ALWAYS develop symptoms and can live with them. Removing them requires surgery, but it's true that surgery isn't necessary until significant symptoms develop. Therefore, if the person can adapt to them and learn to live with their bunion, As long as it does not cause pain, impede footwear, or impair your quality of life, surgery is not necessary..
Who has it?
It is the most common foot deformity, representing a real problem for women, although it is not exclusive to women. For every man who needs surgery, there are 15 women who require treatment.
The typical patient is a woman over 50 years old who has been dealing with her foot for years and takes great care of it, but is now beginning to be bothered, especially by the sole of the foot and the deformity of the smaller toes (not the big one, the others), with the typical hammer toe.
We know that The problem can begin much earlier than one thinks, as many patients explain that the deformity began as early as 10 or 12 years of age., although symptoms may appear from the fourth or fifth decade of life and the average age of surgery is around 60 years.
In most patients, the problem is in both feet, although the magnitude varies greatly on each side.
Heredity is another important factor as it occurs in 60-80% of cases.
In addition to these factors, there are other anatomical and mechanical factors, such as laxity of the ligaments, mobility of some joints, the relationship that may exist with flat feet, which are controversial, but may be involved in this problem.

Symptoms
In addition to an unsightly appearance, pain on the inner side of the foot, where the bunion is located, is the main symptom, causing discomfort when wearing rigid-shaped shoes and tight footwear. This pain is caused by a series of inflammatory events and not by the bump itself, which is a normal bone that protrudes when displaced from its normal location.
Besides, It is common to find that people begin to develop calluses and pain in the sole of their feet, because the function of the feet when walking is affected., changing the support areas; in the same way, if it progresses for a long time, it may be accompanied by
deformities in the other fingers.
Treatment
Patients are initially treated with all available non-surgical conservative methods, including insoles, various big toe separators, wide, comfortable shoes, rehabilitation, and pain medication. Despite this, some patients persist with discomfort and require surgery to restore the foot's shape and function.
Foot surgery is known for being very painful, with a very cumbersome postoperative period, which is not entirely true today. Improvements in anesthesia techniques, the refinement of surgical techniques, the use of bandages, as well as special footwear, and improved medical treatment of postoperative pain make this belief somewhat outdated today.
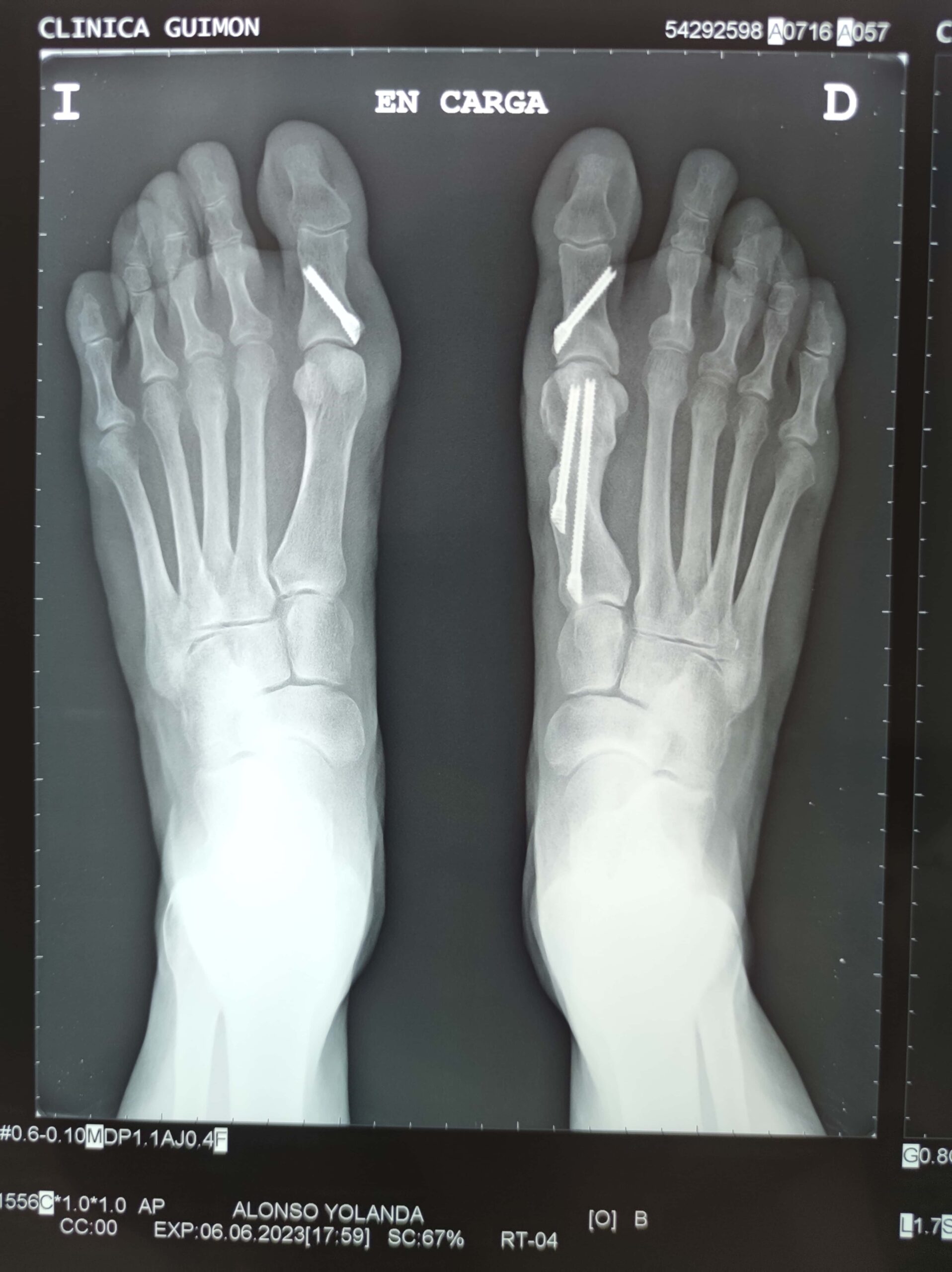
The surgery involves incisions in the bones to achieve proper alignment of the big toe, using screws or other materials to maintain the reconstruction.
Surgery is typically performed through very small incisions, called percutaneous (minimally invasive) surgery, sometimes incorrectly referred to as laser surgery. Sometimes we also have to resort to standard open surgery. The technique will depend on each specific case, as every surgery has its indication.
We know that the problem can begin much earlier than expected, as many patients report that the deformity began as early as 10 or 12 years of age, even though symptoms can appear as early as the fourth or fifth decade of life and the average age for surgery is around 60 years.
In most patients, the problem affects both feet, although the severity varies greatly on each side. Heredity is another important factor, as it occurs in 60–80% of cases.
In addition to these factors, there are other anatomical and mechanical factors, such as ligament laxity, joint mobility, and the possible relationship with flat feet, which are controversial but may be involved in this problem.